ABOUT BONDED NEODYMIUM
For a more flexible alternative to sintered neodymium, consider using bonded neodymium magnets for your application. Bonded neodymium powder is used to create these magnets. Powder is melted and mixed with a polymer. Components are then pressed or extruded to create the product. Bonded Neodymium magnets can be magnetized into complex patterns with multiple poles. Though much weaker than Sintered Neodymium magnets, Bonded neodymium magnets give greater flexibility in terms of shapes that can be made. They are also lighter than Samarium Cobalt, and have a lower acceptable temperature (coercivity). Nevertheless, they offer excellent value for applications that require a smaller magnet or utilize radial rings.
Applications include automotive, home, power tools, as well as electronic industries.
Bonded neo radial ring
Traditionally, multi-pole sintered Neo ring magnets were created using multiple arc magnets glued to the assembly. While spinning, it was not uncommon for the adhesive material to loosen and the magnet would dislodge itself. Also, the requirements for accuracy between all of the magnets in the ring shape required the exact same physical and magnetic properties – thus many magnets would fail because of the lack of homogeneity.
A better way is to create circular magnets with uniform poles. By creating just one single magnet specifically designed for your application, we are able to provide your company a product that is stronger, more reliable, and more efficient. The magnets are multi-pole – which does not compromise the magnetic properties. Contact your Yunsheng sales representative to learn more about how this technology may help your company today!
APPLICATION
- Stepper motors
- Actuators
- Magnetic bearings
- Steering control motors
- Magnetic clutch
- Peripheral motors
- Spindle motors
ADVANTAGES
- Geometric precision
- Variety of magnetic configuration
- Homogeneous distribution of magnetic field
- Design and assembly simplification
- Precision of motor performances
- Cost efficiency
- Huge marketing potential
Magnetic Force
 Regular Magnet |
 Radial Orientation |
Magnetic Orientation
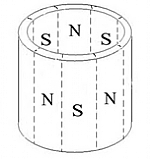 Multiple Poles |
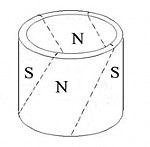 Skewed Magnetization |
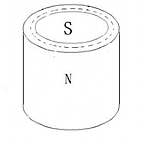 Single Pole |

Products
Compression Molded BONDED NEODYMIUM GRADES
|
Grade |
Residual Induction |
Coercive Force |
Intrinsic Coercive Force |
Maximum Energy Product |
Density D |
Reversible Permeability |
Reversible Temp Coefficient A |
Max Operating Temp |
|
BNP-2 |
300-400 |
160-240 |
440-600 (5.5-7.5) |
19-26 |
5.6-6.0 |
1.20 |
-0.11 |
160 |
|
BNP-3 |
400-510 |
216-280 |
504-680 |
24-32 |
5.6-6.0 |
1.20 |
-0.11 |
160 |
|
BNP-4 |
460-520 |
224-288 |
504-680 |
30-35 |
5.6-6.0 |
1.20 |
-0.11 |
160 |
|
BNP-5 |
470-550 |
240-360 |
520-680 |
37-44 |
5.6-6.0 |
1.20 |
-0.11 |
160 |
|
BNP-6 |
550-650 |
320 – 376 (4.0 – 4.7) |
600-720 |
44-52 |
5.6-6.0 |
1.20 |
-0.11 |
160 |
|
BNP-7 |
550-650 |
320-408 |
560-680 |
52-64 |
5.6-6.0 |
1.20 |
-0.11 |
160 |
|
BNP-8 |
620-670 |
400-456 |
640-800 |
64-76 |
5.8-6.2 |
1.20 |
-0.11 |
160 |
|
BNP-8A |
620-680 |
400-480 |
1040-1280 |
65-73 |
5.8-6.1 |
1.20 |
-0.10 |
180 |
|
BNP-9L |
670-730 |
360-416 |
520-640 |
68-75 |
5.8-6.1 |
1.20 |
-0.11 |
120 |
|
BNP-9 |
650-700 |
416-456 |
680-800 |
68-76 |
5.8-6.2 |
1.20 |
-0.12 |
160 |
|
BNP-9H |
650-700 |
432-488 |
920-1040 |
71-80 |
5.8-6.1 |
1.20 |
-0.10 |
180 |
|
BNP-10H |
650-710 |
432-480 |
764-960 |
74-82 |
5.8-6.1 |
1.20 |
-0.10 |
180 |
|
BNP-10 |
670-720 |
424-480 |
640-800 |
76-84 |
5.8-6.2 |
1.20 |
-0.10 |
160 |
|
BNP-11 |
680-740 |
400-480 |
640-800 |
80-88 |
6.0-6.2 |
1.20 |
-0.10 |
160 |
|
BNP-12D |
720-770 |
440-520 |
720-880 |
88-96 |
6.1-6.3 |
1.20 |
-0.10 |
160 |
|
BNP-12L |
730-770 |
368-432 |
520-640 |
80-88 |
6.0-6.3 |
1.20 |
-0.12 |
120 |
|
BNP-13L |
780-830 |
400-480 |
480-640 |
88-104 |
6.1-6.4 |
1.20 |
-0.12 |
120 |
Injection Molded BONDED NEODYMIUM GRADES
|
Grade |
Residual Induction |
Coercive Force |
Intrinsic Coercive Force |
Maximum Energy Product |
Density D |
Reversible Permeability |
Reversible Temp Coefficient A |
Max Operating Temp |
|
BNI-3 |
350-450 |
200-280 |
400-640 |
20-28 |
4.5-5.0 |
1.20 |
-0.11 |
120 |
|
BNI-4 |
400-500 |
240-320 |
560-720 |
28-36 |
4.5-5.0 |
1.20 |
-0.11 |
120 |
|
BNI-5 |
450-550 |
304-360 |
640-800 |
36-44 |
4.5-5.1 |
1.20 |
-0.11 |
120 |
|
BNI-5SR |
450-550 |
320-400 |
880-1120 |
36-44 |
4.8-5.3 |
1.20 |
-0.11 |
180 |
|
BNI-6 |
500-600 |
328 – 384 (4.1 – 4.8) |
640-800 |
44-52 |
4.7-5.2 |
1.20 |
-0.11 |
120 |
|
BNI-6SR |
500-600 |
320-408 |
880-1120 |
44-52 |
4.9-5.4 |
1.20 |
-0.11 |
180 |
|
BNI-7 |
550-650 |
344-400 |
640-800 |
52-60 |
4.7-5.3 |
1.20 |
-0.12 |
120 |
